Aqueous Solution
Aqueous solutions are primarily composed of water, with small amounts of additives included to enhance rust protection and lubrication. These solutions offer excellent cooling properties and are commonly used in general grinding and other finishing operations. The formulation is clear, allowing operators to easily monitor the process. However, pure water tends to cause metal corrosion and lacks sufficient lubrication. To address this, specific additives are often incorporated into the aqueous solution to maintain effective cooling, while also providing good rust resistance and some level of lubrication.

2. Emulsion
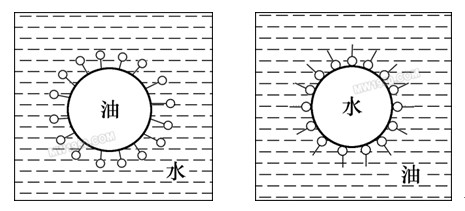
Emulsions are created by diluting emulsified oil with water. This oil typically contains mineral oil, an emulsifier, and various additives. When mixed with 95% to 98% water, it forms a milky or translucent liquid. Although emulsions provide good cooling, their high water content results in weaker lubrication and rust prevention. To improve these properties, oily additives, extreme pressure agents, and rust inhibitors can be added to create specialized emulsions such as extreme pressure or anti-rust types. An emulsifier acts as a surfactant, helping to blend oil and water by reducing the interfacial tension between them. It has a hydrophilic (water-attracting) end and a lipophilic (oil-attracting) end, which allows it to stabilize the mixture by positioning itself at the oil-water boundary. This creates a stable oil-in-water emulsion, commonly used in metal cutting applications, as shown in the image below.
Schematic diagram of oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsion
Low-concentration emulsions are ideal for cooling-intensive tasks like grinding, drilling, and rough machining. High-concentration emulsions, on the other hand, offer better lubrication and are typically used for precision operations such as threading, boring, and gear shaping.
3. Cutting Oil
Cutting oils are mainly made from mineral oil, though some formulations use animal or vegetable oils or compound oils. Pure mineral oil does not form a strong lubricating film under friction, resulting in average lubrication performance. In practice, additives such as extreme pressure agents and rust inhibitors are often included to improve both lubrication and corrosion resistance. Animal and vegetable oils have good lubricity and are suitable for low-speed finishing, but they are prone to oxidation and degradation over time. Therefore, it's best to limit their use or replace them with more stable alternatives, such as mineral oils containing sulfur or chlorine-based extreme pressure additives. For normal turning and tapping, standard oils work well. Kerosene is preferred for finishing non-ferrous metals or cast iron, while vegetable oils may be used for threading operations. Adding appropriate oily and extreme pressure additives to mineral oil enhances its performance under high temperature and pressure conditions, making it suitable for finishing, reaming, tapping, and gear processing.
Colorful Doorbell,Eco Friendly Doorbell,No Battery Wireless Doorbell,Energy Harvesting Doorbell
Foshan Shunde Advante Electron Ltd. , https://www.china-advante.com